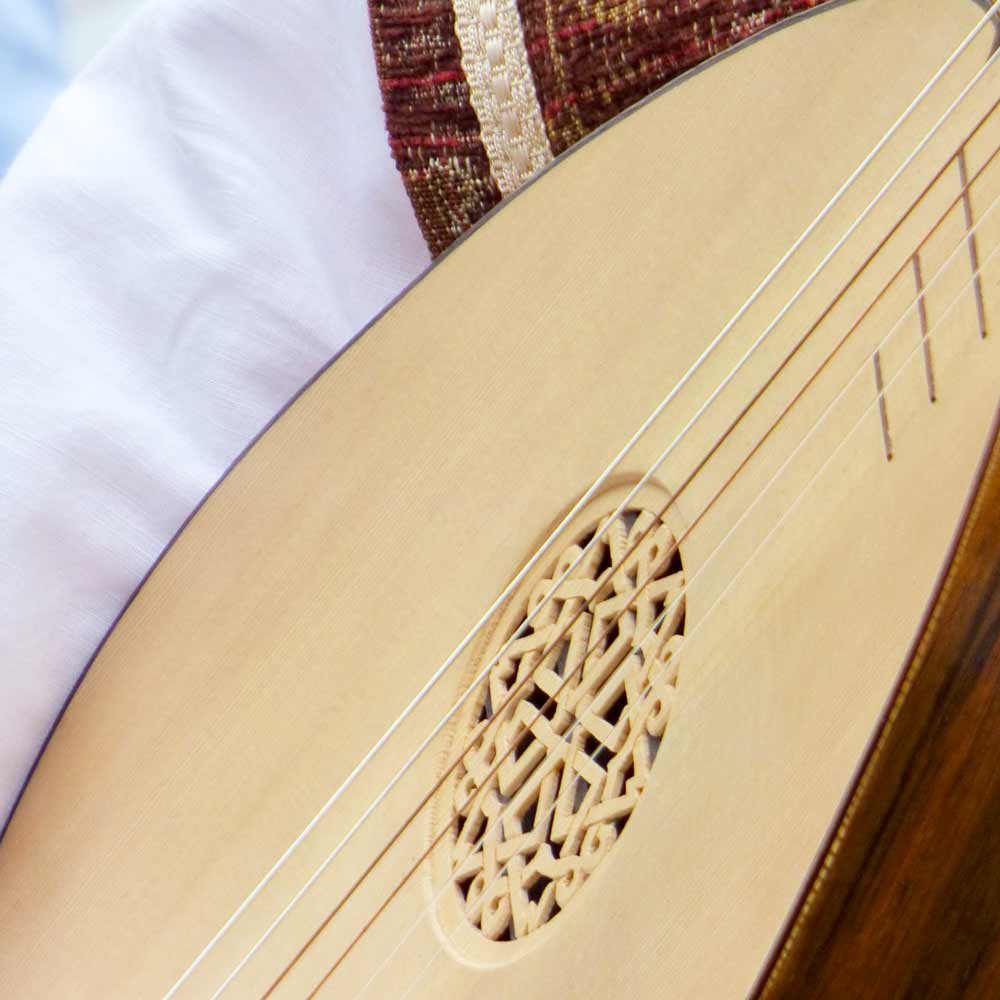
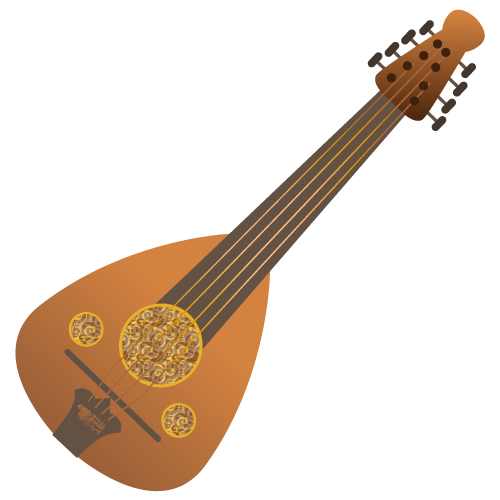
The oud is an oval-shaped stringed instrument that is similar in appearance to a lute. The modern oud is a close relative of the Assyrian Lute and many similar instruments from the Middle East and North African regions. An important characteristic of the oud is its lack of frets and its short neck. Scholars have estimated that the emergence of the oud dates to the 3rd century AD within Central Asia. It is thought to have derived from a very similar instrument known as the Barbat that was already in use in pre-Islamic Persia. Munir Bashir is known as 'the king of oud.' This Iraqi Assyrian musician used an Arabian Oud and he incorporated a variety of influences into his improvised style. He experimented with various styles of oud tuning and had his own particular type of light pick or 'reesha' in Arabic. Another famous oud player is Naseer Shamma, also from Iraq. Naseer has toured all over the world and also runs his own music school in Cairo.
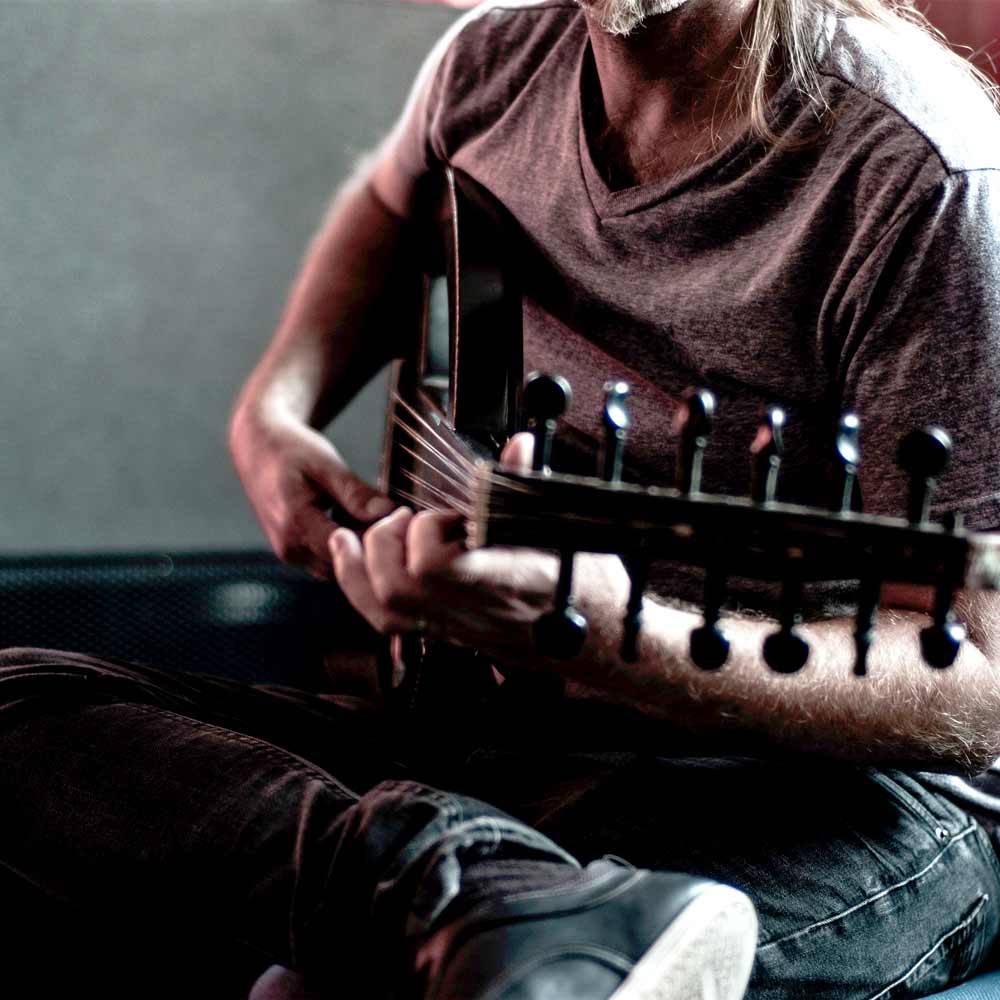

Oud means "from wood" and "stick" in Arabic. There are three different types of oud, Arabian, Turkish, and Persian. Ouds from Arabia are the larger of the three types and produce deeper sounds. Ouds of Turkish origin tend to be smaller and produce sounds at a higher pitch.

Although ouds are associated with traditional Arabian music, their versatile sound can be enjoyed in a variety of different types of music. So, where a song may usually feature a guitar, try it with an oud and see how the sound changes how you experience the song.
Experience the oud in less than one minute, anywhere, anytime. You can use your computer, tablet or even mobile device.
Anyone can play the oud through Virtual Piano. You don’t need to be able to read music or to have played the oud before. Virtual Piano music sheets contain letters that correspond to the keys from a QWERTY keyboard. So it’s quick and simple to pick up. You can enjoy playing the oud instantly - anywhere, anytime.